Registration of Foreign Companies in India: A Step-by-Step Guide
India is an attractive destination for foreign companies looking to expand their global footprint, thanks to its large market, skilled workforce, and favorable business environment. However, registering a foreign company in India can be a complex process that requires careful planning and adherence to the country’s regulatory requirements. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the necessary steps, required documents, and key considerations for successfully registering a foreign company in India. Lets dive into details about Registration of Foreign companies in India
Table of Contents
- Types of Entities for Registration of Foreign Companies in India
- Steps to Register a Foreign Company in India
- Documents Required for Registration
- Post-Registration Compliance
- Key Considerations for Foreign Companies
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Types of Entities for Registration of Foreign Companies in India
Before registering a foreign company in India, it’s essential to understand the different types of business entities available. The two most common structures for foreign companies are:
Section 2(42) of the Companies Act, 2013, defines a foreign company as a company or a body corporate incorporated outside India and which has a place of business whether by itself or through an agent, in this country. Foreign nationals/ Foreign Companies can form a company in India through any of entry strategy mentioned below (India Subsidiary Registration)
- Wholly Owned Subsidiaries ( 100% Indian Subsidiary )
- Joint Ventures with other Indian Companies in case 100% FDI is not permitted
- Liaison Office (LO): An LO serves as a representative office for the foreign parent company in India. It’s primarily responsible for promoting the parent company’s business interests, providing information about its products and services, and facilitating communication between the parent company and Indian customers. However, an LO is not permitted to engage in any profit-making activities in India.
- Branch Office (BO): A BO is an extension of the foreign parent company and can engage in a wider range of business activities, including marketing, import and export, and technical support services. However, a BO is generally restricted from manufacturing and processing activities in India. Profits earned by a BO are subject to Indian taxation.
- Other options for foreign companies include setting up a Project Office, a wholly-owned subsidiary, or a joint venture with an Indian partner. The choice of entity depends on the foreign company’s business objectives, investment plans, and risk appetite.
Steps to Register a Foreign Company in India
Here’s a step-by-step guide to registering a foreign company in India:
- Obtain a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC): The first step in the registration process is obtaining a DSC for the company’s authorized representatives. A DSC is an electronic signature used for filing documents and forms online with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
- Obtain a Director Identification Number (DIN): Each director of the foreign company must obtain a DIN, which is a unique identification number issued by the MCA. The DIN application form can be filed online, and the required supporting documents must be submitted along with the application.
- Reserve the company name: You must reserve a unique name for your foreign company with the Central Registration Centre (CRC) of the MCA. You can submit the name reservation application through the MCA’s online portal. Ensure that the proposed name complies with the naming guidelines laid down by the MCA.
- Prepare and file the incorporation documents: Prepare the necessary incorporation documents, such as the Memorandum of Association (MoA) and Articles of Association (AoA). These documents must be filed electronically with the MCA, along with the required fees and supporting documents.
- Obtain a Permanent Account Number (PAN) and Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN): After your foreign company is registered, you must obtain a PAN and TAN for tax purposes. These numbers are essential for complying with Indian tax laws and regulations.
- Open a bank account: Open a bank account in India for your foreign company to facilitate financial transactions. You may be required to provide the Certificate of Incorporation, PAN, and other relevant documents to open the account.
- Register for applicable taxes: Depending on the nature of your business activities, you may need to register for various taxes, such as Goods and Services Tax (GST), Professional Tax, and others. Ensure that your foreign company is registered for all applicable taxes to maintain compliance with Indian tax laws.
- Obtain necessary licenses and permits: Depending on your business sector and activities, you may need to obtain specific licenses and permits to operate in India. Research the requirements for your industry and ensure that you have all the necessary approvals in place before commencing operations.
Documents Required for Registration
When registering a foreign company in India, you’ll need to provide the following documents:
- Proof of the foreign company’s existence, such as a Certificate of Incorporation or equivalent document
- MoA and AoA of the foreign company
- Board resolution authorizing the establishment of the Indian entity
- Power of Attorney issued in favor of the authorized representative in India
- Identity proof and address proof of the directors and authorized representative
- Consent letters from the directors
Note that all foreign documents must be notarized and apostilled (or consularized) in the country of origin, and translated into English if they are not in English.
Post-Registration Compliance
Once your foreign company is registered in India, it’s essential to maintain compliance with the country’s regulatory requirements, such as:
- Filing annual financial statements and returns with the MCA
- Complying with Indian tax laws and filing tax returns on time
- Maintaining proper accounting records and statutory registers
- Complying with labor laws, environmental regulations, and other sector-specific requirements
Key Considerations for Registration of Foreign Companies
Before registering your foreign company in India, keep the following considerations in mind:
- Research the market thoroughly and assess the potential demand for your products or services in India
- Understand the legal, tax, and regulatory environment in India and ensure that your company complies with all relevant requirements</>
- Choose the appropriate business entity based on your company’s objectives, investment plans, and risk appetite
- Consider partnering with a local expert or consultant to help navigate the registration process and post-registration compliance requirements
- Be prepared for potential challenges, such as cultural differences, language barriers, and bureaucratic hurdles
- Develop a long-term strategy for your company’s growth and success in the Indian market
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can a foreign company operate in India without registering a local entity?
A foreign company can conduct business in India without registering a local entity only in specific cases, such as through the export of goods and services, or by entering into contracts with Indian companies. However, to establish a physical presence and carry out a broad range of business activities in India, registering a local entity is generally required.
2. Can a foreign company own 100% of an Indian subsidiary?
Yes, a foreign company can own 100% of an Indian subsidiary in most sectors, subject to the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy of the Government of India. However, there are certain sectors where FDI caps or restrictions apply. It’s essential to consult the latest FDI policy to understand the specific requirements for your industry.
3. How long does it take to register a foreign company in India?
The registration process for a foreign company in India can take anywhere from a few weeks to a few months, depending on the complexity of the case and the efficiency of the authorities involved. It’s crucial to plan ahead and factor in the time required for registration when entering the Indian market.
4. Can a foreign company repatriate its profits from India?
Yes, a foreign company can repatriate its profits from India, subject to compliance with the applicable regulations and payment of necessary taxes. Profits can be repatriated in the form of dividends, royalties, or fees for technical services, among other channels. It’s essential to consult with a tax expert to understand the specific requirements for repatriation of profits from India.
Conclusion
Registering a foreign company in India can be a complex and time-consuming process, but with the right guidance and understanding of the regulatory requirements, it can be a rewarding endeavor. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you’ll be better prepared to navigate the registration process and successfully establish your foreign company in the booming Indian market.
Steps for forming a Private Limited Company Registration (Foreign company registration ):
Registering a private limited company requires a support of CA/CS/Lawyer as the legal procedures are involved in it, it’s a complicated process but do not worry our team of experts will take care of these issues
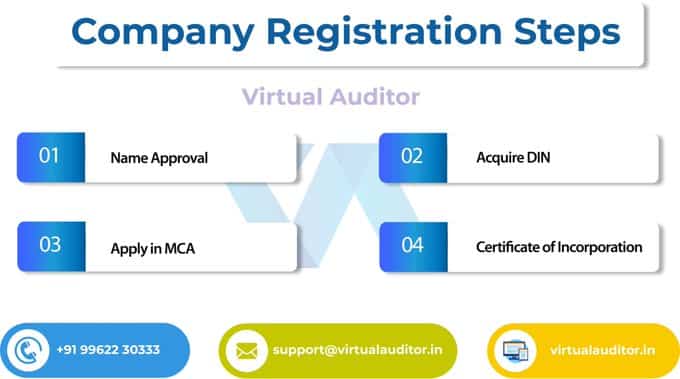
India offers companies a large, built-in and dynamic potential market to explore. If you are interested in conducting business in this market, you need to establish your company’s legal presence in India by registering your business and filing the appropriate forms with the proper Indian authorities. In case of any help or assistance in Foreign Company registration in India , contact Virtual auditor support team on
9962 260 333/9962 230 333 /mail us support@virtualauditor.in, our team will guide through the entire process and help you comply


They have given a step by step process on foreign company registration in India such as certificates documents needed for foreign registration and how to register a foreign company in india as a subsidiary company.